|
VAT RED 1 |
| Synonyms. Vat Red 1; 6-Chloro-2-(6-chloro-4-methyl-3-oxobenzo(b)thien-2(3H)- ylidene)-4- -methylbenzo(b)thiophen-3(2H)-one; CI 73360; Vat Pink R; D & C Red No. 30L; 5,5'-Dichloro-3,3'-dimethyl-thioindigo; Amanthrene Pink FF; Calcophyl Red FF; Vat Pink FF; Other RN: 77642-23-0, 84136-96-9, 88507-36-2 |
|
|
| PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION | |
|
CAS RN |
2379-74-0 |
|
EINECS RN |
219-163-6 |
|
FORMULA |
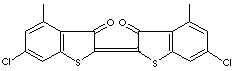
C18H10Cl2O2S2 |
|
MOLE WEIGHT |
393.31 |
|
H.S CODE |
3822.00.5090 |
|
SMILES |
C1(=C2/C(c3c(cc(cc3S2)Cl)C)=O)\C(c2c(cc(cc2S1)Cl)C)=O |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
|
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
|
| PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES | |
|
PHYSICAL STATE. |
Red powder |
|
MELTING POINT |
|
|
BOILING POINT |
|
|
DENSITY |
|
|
SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
0.03 mg/l |
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | |
|
VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
log P(octanol-water) |
5.92 |
|
VAPOR PRESSURE |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION TEMP |
|
| pH |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
|
|
| STABILITY AND REACTIVITY | |
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions. |
|
INCOMPATIBLE MATERIALS |
Strong oxidizing agents |
| POLYMERIZATION |
Has not been reported |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2,Flammability:1, Reactivity: 0 |
|
|
| EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|
Wikipedia Linking - Vat dye Google Scholar Search - Vat Red 1 Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Vat Red 1 PubChem Compound Summary - Vat Red 1 KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Vat Red 1 http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Vat Red 1 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Vat Red 1 http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/ http://www.ifc.net.au/ http://www.colorantshistory.org/
|
|
|
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
|
APPEARANCE |
red powder |
|
STRENGTH |
100.0% ± 3.0% |
|
Fe |
200ppm max |
|
FASTNESS |
Light (3-4), Wash (4) |
|
MOISTURE |
1.0% max |
|
|
| TRANSPORT & REGULATORY INFORMATION | |
|
UN NO. |
3077 |
| HAZARD CLASS |
9 |
| PACKING GROUP | III |
|
|
| SAFETY INFORMATION | |
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
May be harmful if inhaled. May cause respiratory tract irritation. May be harmful if absorbed through skin. May cause skin irritation. May cause eye irritation.May be harmful if swallowed. |
|
GHS |
|
|
SIGNAL WORD |
Warning |
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H440-H413 |
|
P STATEMENTS |
P273 |
|
|
| PACKING |
|
|